
#GIT VS SUBVERSION INSTALL#
To import SVN repositories it is required to specify the repo source parameter type to git-svn for the corresponding entries. VS Code will use your machines Git installation (at least version 2.0.0 ), so you need to install Git first before you get these features. Starting new repositories or getting started with one. Will be overridden by an update/install process (like an implicit -force for each Gitman command). Lists the repository URL (see below), the checked out revision number etc. In this matter any changes in the imported svn repository The focus of this feature is to just import SVN dependencies Git is a distributed version control system so, unlike SVN, creating a branch does not make it available to other people. The Gitman git svn support does currently not track any changes in the imported SVN repository. The Git system helps in merging the files quickly and also assist in finding the unmerged ones. This tool allows you to use Git as a valid client to a Subversion server, so you can use all the local features of Git and then push to a Subversion server as if you were using Subversion locally. It's a distributed version control system. One of Git’s great features is a bidirectional bridge to Subversion called git svn. If you're considering switching from SVN to Git, you'll want to take these into account. There are also key differences in repositories, branching, and more. It’s also very similar in many ways to CVS, which was the big boy of the source-control world before that. The biggest difference between Git vs Subversion (SVN) is that Git version control is distributed while SVN is centralized.
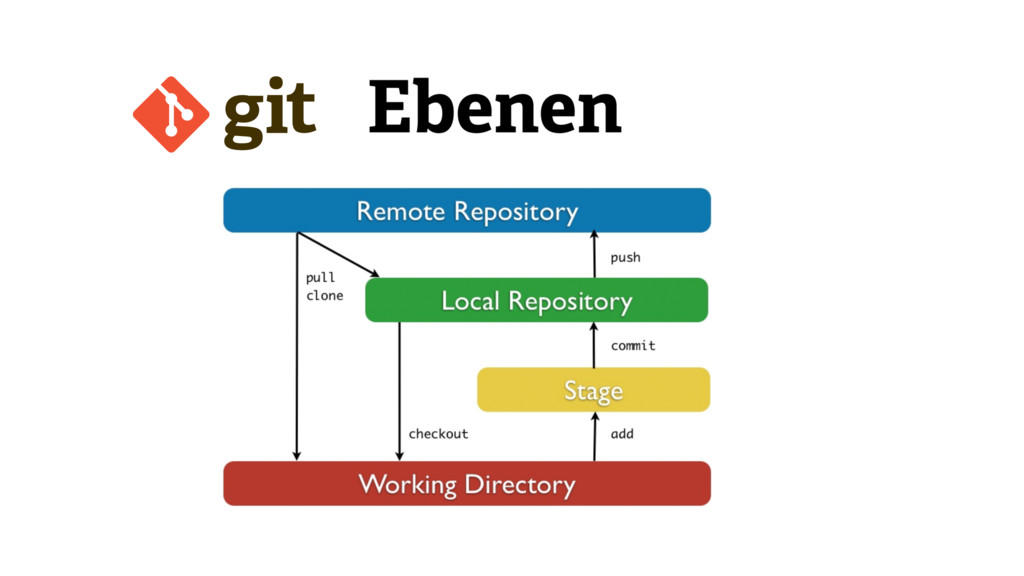
It’s the most popular open source VCS and has been around for nearly a decade. Many development projects use Subversion (SVN) to manage their source code.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
